Off-grid solar power systems
An off-grid solar power system is one that gets most or all of its electricity from the sun using solar panels (photovoltaic panels) and none from a power utility such as a hydroelectric dam, nuclear, coal or natural gas fired plant, ... The grid, which the system is "off" of, refers to the complex network of power lines that connect the utilities to the numerous buildings that use the power. Since in many locations there may be clouds for days or weeks at a time, off-grid systems usually have a back-up generator as well. In addition they may have wind turbines, microhydro and other small electricity generating means.
The following is a simplfied diagram of an off-grid system.
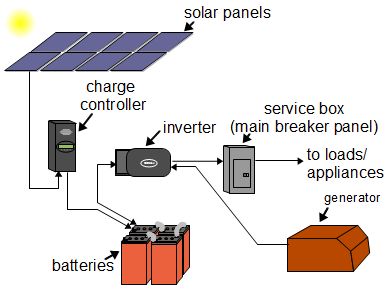

The various parts are:
- solar panels - These take the solar energy from the sun and turn it into electrical energy, electricity.
- batteries - Since the sun doesn't always shine, the electrical energy has to be stored somewhere for use in the meantime. We store it in batteries.
- charge controller - This controls charging of the batteries, similar to how as a cell phone charger controls charging of a cell phone.
- service box - This part you should be familiar with since you already have one of these. This is your breaker panel with all your breakers in it for in case there is an electrical short somewhere.
- loads/appliances - Your lights, fridge, fans, clocks, ...
- generator - A diesel, propane or natural gas generator for generating power in case there hasn't been sun for a long time and the batteries are dead. This will provide elecricity when that happens.
- inverter - Takes the power in the batteries and converts it into a form suitable for your loads/appliances. It also takes power from the generator and passes some through to your loads/appliances and uses some to charge the batteries.
Below is an off-grid system showing an inverter, charge controller, lightning arresters, control boxes and a battery bank. I helped install this one and the one in the photo of solar panels above for Ottawa Solar Power.


Here's another diagram with more of the parts filled in.
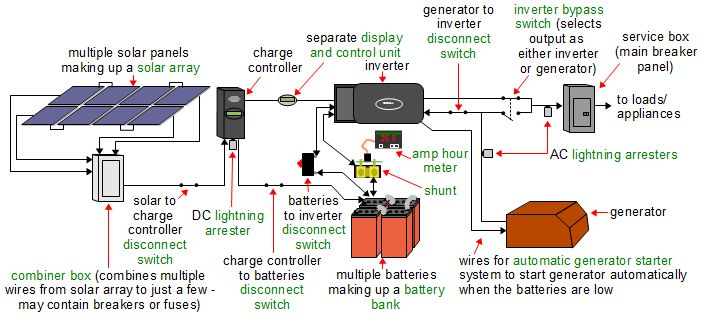
The added parts are as follows:
- solar array - If there are multiple solar panels in a system then they're collectively referred to as a solar array.
- battery bank - Multiple batteries in a system are referred to as a battery bank.
- disconnect switches - Throughout the system there are switches that are normally closed but are in place in case a part needs to be isolated for repairs and to prevent a short circuit in the system from damaging parts. For example, the charge controller has disconnect switches to either side of it.
- inverter bypass switch - If the solar system can longer supply power to the loads then this allows the generator to take over while the solar system is repaired.
- lightning arresters - Lightning arresters are on any wires that may bring damaging electrical current into the system from lightning. For example, if lightning strikes the solar panels then the panels will be damaged but the lightning arrester at the charge controller should protect it.
- combiner box - Depending on the number of solar panels and how they're wired up, it may make sense to have a box near the panels that combines many of the wires coming from them into just a few wires for the long distance to the charge controller.
- display and control unit - Some systems allow networking of their components so that they can be controlled and monitored from a single box, usually with an LED display. For example, OutBack's MATE and Magnum Energy's Remote Control.
- shunt - Part needed if you're going to be using an amp hour meter or battery monitor of some sort. Allows for monitoring of current going into and coming out of the battery bank. See the amp hour meter page for more details.
- amp hour meter - A device that monitors the battery's state of charge (SOC) by measuring the electrical current going in or out of the battery bank. Also referred to as a battery monitor. See the amp hour meter page for more details.
- automatic generator starter - If the batteries are low and there is no sun then the generator is run to top up the batteries and take over supplying power to the loads. This can either be done manually or be done automatically as a feature of the inverter, charge controller, display and control unit (e.g. OutBack's products) or a standalone automatic generator starter box (e.g. Magnum Energy's Auto Generator Start Controller.)
Additional components not shown above are those needed for powering pumps using solar which you can learn about on the solar pumping page, including pump sizing.
And of course you need wires that are appropriate sizes both for safety reasons and to make sure you get the required performance. For the latter, see the page about sizing wires to maintain the necessary voltage over long distances such as from the solar array to the charge controller by calculating the voltage drop.
Designing/sizing an off-grid solar power system
A number of online calculators have been developed and made available here to help you design your off-grid system. They are very detailed and will require real time and focus to complete. This is an iterative process in that results from one calculator may make you go back and redo calculations in other calculators. Each will open in its own window/tab and clicking on links in the body section of those pages will also open new windows/tabs so that you don't lose your work.
Maintaining an off-grid solar power system
And off-grid system is not plug-and-play. The solar panels need to be kept clean, the generator needs to be kept fueled and to have its oil changed periodically, and the batteries needs all sorts of maintenance to keep them working well and to have a long life. See these pages on battery maintenance for details on that.
